Lists
Dynamic arrays that can grow or shrink in size. More flexible than regular arrays.
Properties
Section titled “Properties”- Dynamic size: Can grow or shrink during runtime.
- Maintains order: Elements stay in the order added.
- Allows duplicates: Repeated values are permitted.
Operations
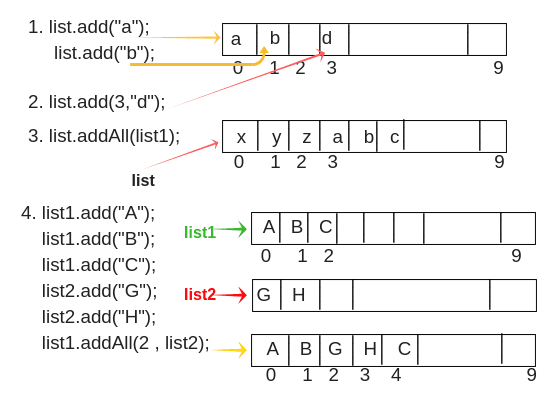
Section titled “Operations”- Access: Directly get an element by its index.
- Insertion: Add an element at the end or at a specific position.
- Update: Change the value of an element at a given index.
- Deletion: Remove an element from the end or from a specific position.
Advantages
Section titled “Advantages”- Dynamic sizing: List can grow or shrink as needed.
- Automatic insertion and deletion: Adding or removing elements will shift other elements.
Disadvantages
Section titled “Disadvantages”- More memory overhead: Lists use extra memory compared to arrays because they store additional information (like capacity, size, and references for dynamic resizing) to support flexible operations.
Example
Section titled “Example”import java.util.ArrayList;
// List of stringsArrayList<String> students = new ArrayList<>();
// Insert elementsstudents.add("Sher");students.add("Riaaz");students.add("Rishika");students.add("Sem");
// Get number of elementsSystem.out.println(students.size()); // Prints 4
// Accessing an elementSystem.out.println(students.get(0)); // Prints "Sher"
// Updating an elementstudents.set(0, "Sherreskly"); // Updates "Sher" to "Sherreskly"System.out.println(students.get(0));
// Deleting an elementstudents.remove(1); // Removes "Riaaz"System.out.println(students.get(1)); // Prints "Rishika"