Linked Lists
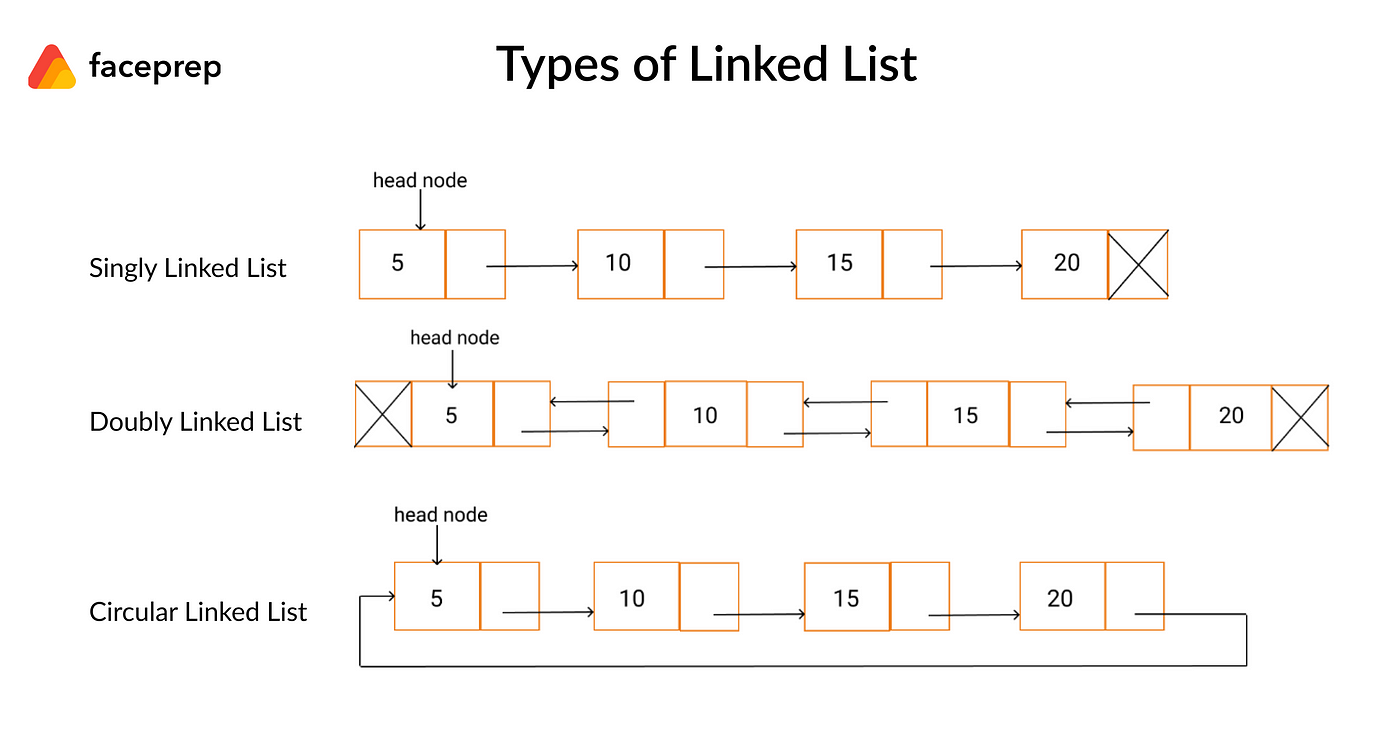
Collection of nodes where each node contains data and a reference to the next node.
- Singly Linked List: One pointer to next node.
- Doubly Linked List: Pointers to both next and previous nodes.
- Circular Linked List: Last node points back to first node.
Use Cases
Section titled “Use Cases”- Music playlists: Songs are linked together, allowing easy addition, removal, and reordering.
- Image viewers: Navigating through images in a gallery uses linked lists for previous/next functionality.
Properties
Section titled “Properties”- Node structure: Each node has data and a pointer to the next.
- Dynamic size: Grows or shrinks as needed.
- Non-contiguous memory: Nodes are scattered in memory.
- No random access: Must traverse from the head.
- Types: Can be singly, doubly, or circular.
Operations
Section titled “Operations”- Access: Traverse from the head to find an element.
- Insertion: Add a new node at a specific position.
- Update: Change the data in a node.
- Deletion: Remove a node from a specific position.
Advantages
Section titled “Advantages”- Dynamic size: The list can grow or shrink as needed.
- Memory allocated as needed: Nodes are created only when required.
- No memory waste: Only necessary memory is used, no pre-allocation.
Disadvantages
Section titled “Disadvantages”- No random access: You cannot directly access an element by index; must traverse from the head.
- Sequential access only: Elements must be accessed one after another, not directly.
- Extra memory for storing pointers: Each node needs additional memory for its pointer(s).
Example
Section titled “Example”import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.ListIterator;
LinkedList<String> songs = new LinkedList<>();
// Insert nodessongs.add("Kendrick Lamar - Not Like Us");songs.add("Alex Warren - Ordinary");songs.add("Drake - Nokia");
// Get number of nodesSystem.out.println(songs.size()); // Prints 3
// Accessing nodesListIterator<String> songsIt = songs.listIterator();while (songsIt.hasNext()) { String song = songsIt.next(); System.out.println(song);}
// Updating a nodeListIterator<String> songsIt2 = songs.listIterator();while (songsIt2.hasNext()) { String song = songsIt2.next(); if (song == "Kendrick Lamar - Not Like Us") { songsIt2.set("Kendrick Lamar - Luther"); }}System.out.println(songs);
// Deleting a nodeListIterator<String> songsIt3 = songs.listIterator();while (songsIt3.hasNext()) { String song = songsIt3.next(); if (song == "Drake - Nokia") { songsIt3.remove(); }}System.out.println(songs);