Arrays
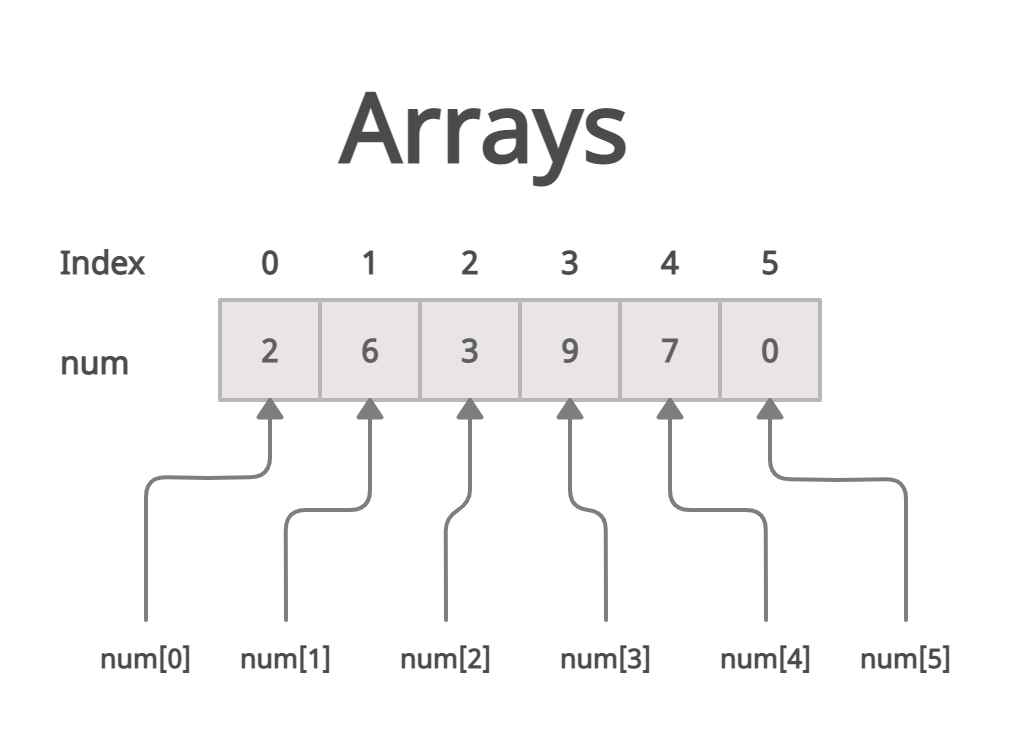
Fixed-size collection of elements of the same type, stored in contiguous memory locations.
Properties
Section titled “Properties”- Fixed size: Size is set when created and cannot change.
- Contiguous memory: Elements are stored next to each other.
- Random access: Any element can be accessed directly by index.
- Same type: All elements must be of the same data type.
- Allows duplicates: Repeated values are permitted.
Operations
Section titled “Operations”- Access: Direct access using index.
- Insertion: Need to shift elements.
- Update: Directly modify an element by index.
- Deletion: Need to shift elements after deletion.
Advantages
Section titled “Advantages”- Fast access: Elements can be quickly accessed using their index.
- Memory efficient: Elements are stored together in memory, reducing overhead.
Disadvantages
Section titled “Disadvantages”- Fixed size: Cannot be resized after creation.
- Manual insertion and deletion: Adding or removing elements requires shifting other elements.
- Memory waste: Unused space is wasted if the array is not fully filled.
Example
Section titled “Example”// Declaration and initializationint[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// Declare and set the size of the arrayString[] students = new String[3];
// Insert elementsstudents[0] = "Dustin";students[1] = "Rewish";students[2] = "Ada Lovelace";
// Accessing an elementSystem.out.println(students[0]); // Prints "Dustin"
// Updating an elementstudents[0] = "Dustin VII"; // Updates "Dustin" to "Dustin VII"System.out.println(students[0]);
// Deleting an elementstudents[2] = null; // Removes "Ada Lovelace"System.out.println(students[2]); // Prints "null"