HashMaps
This content is for DSA. Switch to the latest version for up-to-date documentation.
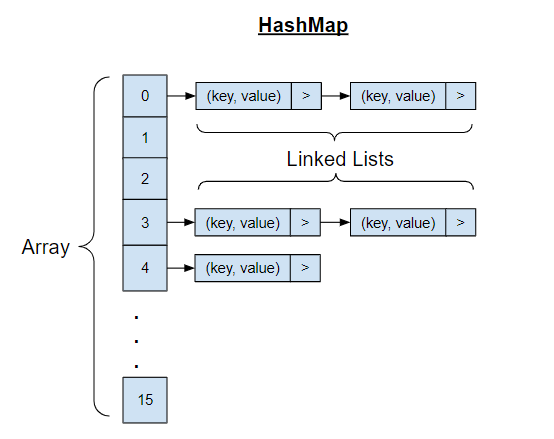
A HashMap is a data structure that stores key-value pairs and uses a hash function to compute an index for fast data retrieval. It’s like a digital phone book where you can quickly find someone’s number (value) by looking up their name (key), regardless of how many contacts you have.
Properties
Section titled “Properties”- Key-value pair storage: Each element consists of a unique key associated with a value.
- Uses hash function to compute index: Keys are converted to array indices using mathematical functions.
- Keys must be unique: No duplicate keys are allowed, but values can be duplicated.
Use Cases
Section titled “Use Cases”- Caching systems: Storing frequently accessed data for quick retrieval.
Operations
Section titled “Operations”- Search: Find a value using its key.
- Insertion: Add a new key-value pair.
- Deletion: Remove a key-value pair.
- Access: Retrieve a value using its key.
- Update: Modify the value associated with a key.
Advantages
Section titled “Advantages”- Very fast average-case operations: Most operations complete in constant time on average.
- Flexible key types: Can use various data types as keys (strings, numbers, objects).
- Dynamic sizing: Can grow and shrink as needed during runtime.
Disadvantages
Section titled “Disadvantages”- No ordering of elements: Elements are not stored in any predictable sequence.
Example
Section titled “Example”import java.util.HashMap;
HashMap<String, Integer> studentGrades = new HashMap<>();
// Insert key-value pairsstudentGrades.put("Swasti", 95);studentGrades.put("Terrence", 87);studentGrades.put("Shafeer", 82);
// Access values using keysSystem.out.println(studentGrades.get("Swasti")); // Prints 95
// Update existing valuestudentGrades.put("Swasti", 100);System.out.println(studentGrades.get("Swasti")); // Prints 100
// Get size of the mapSystem.out.println(studentGrades.size()); // Prints 3
// Remove a key-value pairstudentGrades.remove("Shafeer");System.out.println(studentGrades);
// Iterate through the mapfor (String student : studentGrades.keySet()) { System.out.println(student + ": " + studentGrades.get(student));}