Linear Search
This content is for DSA. Switch to the latest version for up-to-date documentation.
Linear search is the simplest searching algorithm that sequentially checks each element in a list until the target element is found or the entire list has been searched.
Properties
Section titled “Properties”- Sequential access: Examines elements one by one from the beginning
- Works on any data structure: Can be used on arrays, linked lists, etc.
- No sorting requirement: Works on both sorted and unsorted data
- Simple implementation: Easy to understand and implement
How it Works
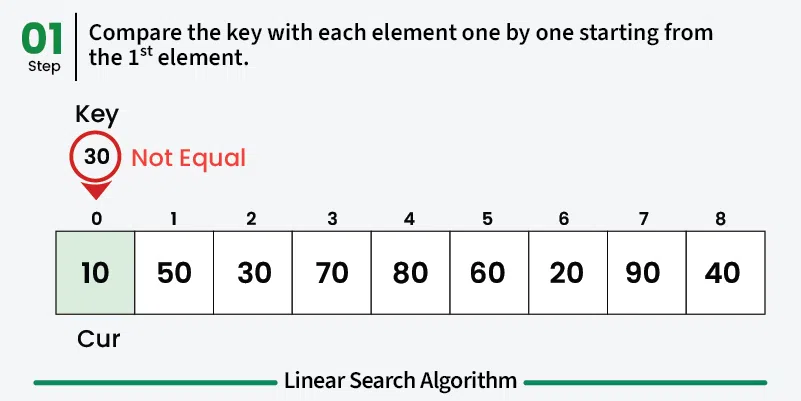
Section titled “How it Works”- Start at the beginning: Begin with the first element of the array
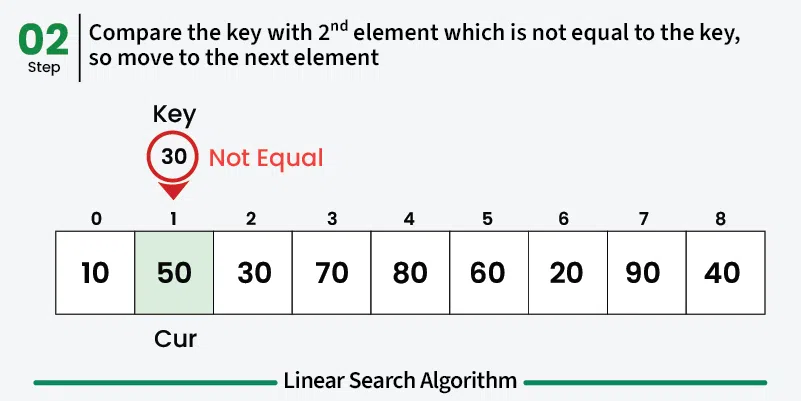
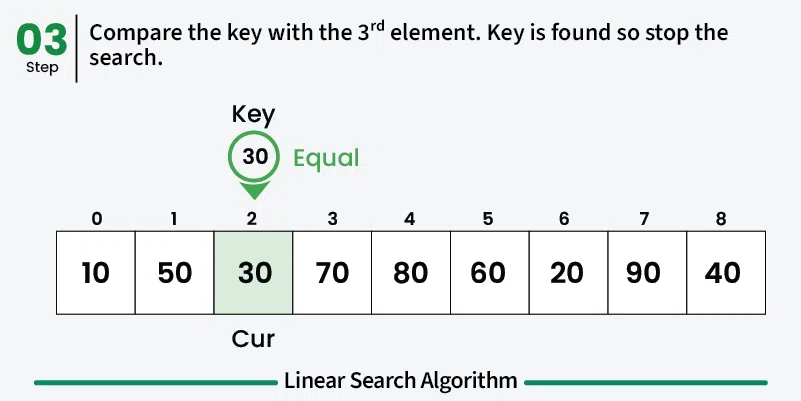
- Compare: Check if the current element matches the target value
- Found: If match found, return the index/position
- Move to next: If no match, move to the next element
- Repeat: Continue until element is found or end of array is reached
- Not found: If end is reached without finding the element, return -1
Use Cases
Section titled “Use Cases”- Small datasets: When the dataset is small and simplicity is preferred
- Unsorted data: When data is not sorted and sorting would be expensive
- One-time search: When searching is done infrequently
- Memory-constrained environments: When memory usage needs to be minimal
Time Complexity
Section titled “Time Complexity”- Best case: O(1) - Element found at first position
- Average case: O(n) - Element found in the middle
- Worst case: O(n) - Element not found or at the last position
Space Complexity
Section titled “Space Complexity”- O(1): Constant space, only uses a few variables
Advantages
Section titled “Advantages”- Simple to implement: Easy to understand and code
- No preprocessing required: Works directly on unsorted data
- Memory efficient: Uses constant extra space
- Works on any data structure: Can be applied to arrays, linked lists, etc.
Disadvantages
Section titled “Disadvantages”- Slow for large datasets: O(n) time complexity makes it inefficient for large data
- Not optimal: Other algorithms like binary search are much faster for sorted data
Example
Section titled “Example”public class LinearSearch { // Method to perform linear search public static int linearSearch(int[] array, int target) {
// 📌 Part 1: Iterate through each element in the array for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
// 📌 Part 2: Check if current element matches the target if (array[i] == target) { return i; // Return the index if found }
}
return -1; // Return -1 if element not found
}
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] numbers = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90}; int target = 22;
System.out.println("Array: [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]"); System.out.println("Target: " + target);
int result = linearSearch(numbers, target);
if (result != -1) { System.out.println("Element found at index: " + result); } else { System.out.println("Element not found in the array"); } }}